Table Of Content
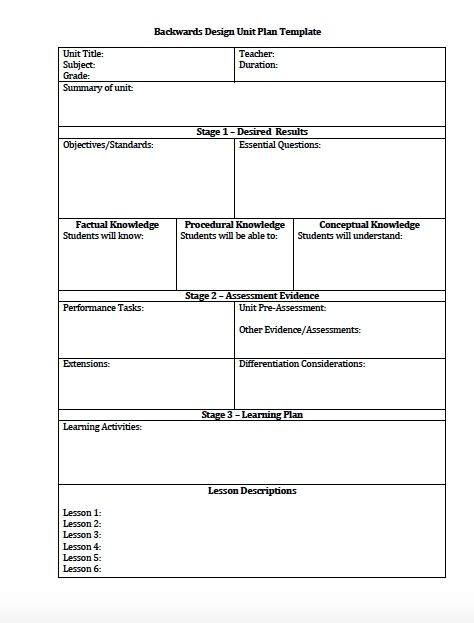
Alignment is the degree to which learning objectives, assessments, learning activities, and instructional materials work together to achieve the desired course goals. For educators looking to align their teaching methods with desired learning outcomes, Backward Design offers a robust, flexible framework. Whether you're teaching in a traditional classroom, a corporate setting, or an online platform, taking the time to plan backward can lead to more effective, engaging, and meaningful learning experiences.
Rigid Framework
Traditional lesson planning begins with teachers looking at standards and learning objectives, and then planning their instructional activities based on those standards. Assessment is often an afterthought, and if implemented at all, it is not always tied directly to the standards or the activities that the students went through. Research strongly suggests, however, that as teachers, we need to begin by looking at the standards and develop content objectives and plan our assessments first. These planned assessments must evaluate whether or not our students mastered the content. Only once the assessments have been planned, can we truly plan the most effective instructional activities. Backward design lesson planning is a process that involves starting with the end goal and then working backward to determine the necessary steps to achieve that goal.
Step 1: Identify the Desired Results
If we don’t plan learning experiences that make that possible, we’re giving them a sub-par education. By focusing on the end goals you want to achieve, then emphasizing assessment types and content, you ensure that your lessons will always teach students what they need to know to pass tests. Depending on your class and what you teach, you may have multiple assessments throughout the course or just one at the very end. If you have just a final assessment, make sure that you model teaching tactics or learning activities toward that test as much as possible. As a result, Blooms Taxonomy guides the lesson planning and helps us frame each lesson with clarity, purpose, and specificity that sets clear expectations. The idea behind backwards design is simply starting from the outcome or end result that you’d like your students to experience and build the modules/chapters/sections one by one with the outcomes guiding the process.
A dynamic resource for goal-centered learning
With this clear target in place, educators are better equipped to teach. A 3-unit, online, self-paced course for K–12 educators interested in planning customized curriculum and/or lesson plans. Consider these questions when planning instruction to move students toward the desired outcome of the unit or lesson. Grant Wiggins and Jay McTighe first introduced the backward design approach to lesson planning in their book Understanding by Design, first published in 1998. While you could spend endless hours digging into their pedagogy and rationale, you don’t need to read the entire book to reap the benefits of this approach.
Daily Fantasy Football Strategy Guide for DFS Beginners - The Fantasy Footballers
Daily Fantasy Football Strategy Guide for DFS Beginners.
Posted: Thu, 04 Aug 2022 07:00:00 GMT [source]
I taught that book a few times, and even though I looked forward to it every time, I always finished the unit a little unsatisfied. When I taught seventh grade language arts, one of my favorite things to teach was S.E. After we did some reflecting, writing, and talking, we were ready to start the book.
Backward Design Step 2. Design the Assessment(s)
Some of these might turn out to be not just fun to teach, but also solid in terms of equipping students with knowledge and skills that will last. If we assume that a large portion of a student’s grade is based on the test, then students are not being measured on their achievement of that standard. The standard does not require students to memorize the phases of the moon. Nor does it ask them to “demonstrate knowledge” of how the whole system works.
Information that fits within this question is the lowest priority content information that will be mentioned in the lesson, unit, or course. Okay, so we’ve looked very closely at one small unit for a middle school science class. Let’s take a look at an example to illustrate the difference between a unit planned the traditional, topic-driven way, and the same unit planned with backward design.
As previously stated, backward design is beneficial to instructors because it innately encourages intentionality during the design process. It continually encourages the instructor to establish the purpose of doing something before implementing it into the curriculum. Therefore, backward design is an effective way of providing guidance for instruction and designing lessons, units, and courses. Once the learning goals, or desired results, have been identified, instructors will have an easier time developing assessments and instruction around grounded learning outcomes. Besides the final assessment, teachers can gather evidence of student learning by building regular formative assessments into their lessons or units.
Center for the Advancement of Teaching Excellence
Asking a person to develop a model is a much higher-order task than asking them to copy a model. Describing systems and patterns is way more challenging than selecting the correct description. To connect directly with our partners for teaching support or for help with Ohio State eLearning tools, visit our help forms. Reflect upon the impacts of climate change on their local communities and in their everyday lives.
The purpose behind Blooms Taxonomy is to help us guide our students from learning to acquire new knowledge to more concrete and higher levels of mastery such as application, analysis, critical thinking and evaluation. The first step in beginning to use and incorporate backwards design is to identify the overall course outcomes, not objectives for your learners. One of the best ways to do this is by listing and or writing out outcomes using Bloom’s Taxonomy. One cannot plan curriculum and build learning products without clearly defining the expectations and outcomes for our students. This happens too often and students experience the disconnect between the material and their results feeling lost and or confused because the expectations do not match up. However, the backward design approach provides an authentic learning experience relevant for both the educator and the student when deployed effectively.
Historians use “continuity and change” to refer to aspects of life or society that have remained the same (continuity) or developed over time (change). For the sake of this article I will use two examples as exemplars for each stage of the planning, the Scientific Revolution & Enlightenment and U.S. Next consider what skills they need improvement on that might work with the content. This psychological theory was developed by Edward L. Deci and Richard M. Ryan in the late 1970s and early 1980s. Self-Determination Theory emphasizes the importance of people feeling in control of their actions, and it posits that this autonomy leads to increased motivation and better outcomes.
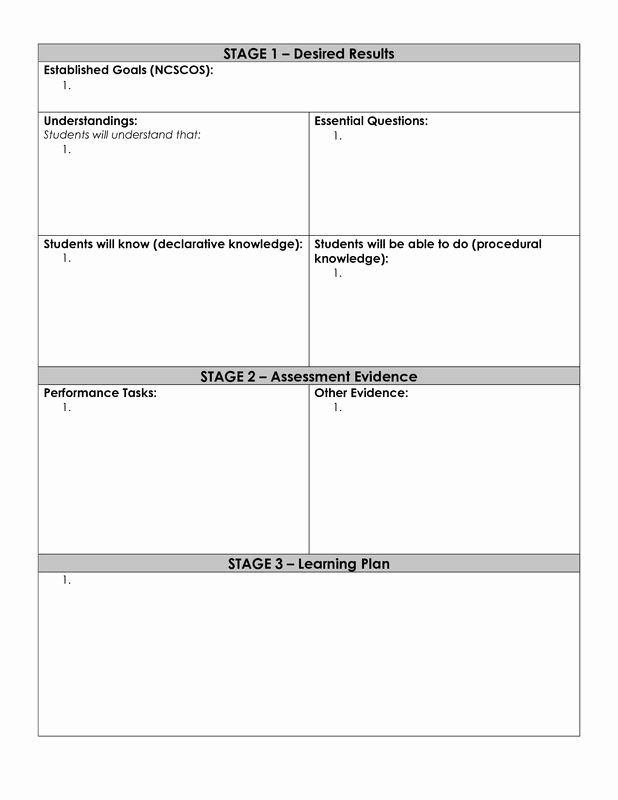
Finally, each lesson in the unit is planned to address at least one of the culminating objectives. Develop a sequence of lessons and activities that help students develop and practice the skills needed to achieve the learning goal. This step is all about setting students up for success on the end-of-unit assessment. So, if a lesson or assignment doesn’t fit the mold, chances are it’s not needed. After an exam, for instance, instructors might hear students express their frustration with statements such as, “that test wasn’t fair” or “that question came out of left field”.
Since you need to track student progress with respect to all course goals and learning outcomes, each outcome should be tested by at least one assessment of student learning. It should be possible to think of several ways to assess a given learning outcome—if you can only think of one way to assess an outcome, then it is probably an assignment. When using the Step-by-Step Guide below to plan your course, you'll want to keep your ideas organized. A Course Plan template like the one pictured here helps you outline your course week-by-week, articulate how you will sequence course content, and solidify the timing of learning activities over the semester. Complete the columns of the template in order as you proceed through each step of backward design. Laying out your Course Plan this way will enable you to see the big picture as you work, so you can ensure that all components of your course stay aligned.


No comments:
Post a Comment